Fazlul Haq, an advocate, was suffering from Interstitial Lung Disease since last two years. It took him at least 2 months in hospital to recover from COVID. – Cheena Kapoor
During the winter months, it’s hard to tell whether the sun rises at all in the New Delhi neighbourhood of Sukhdev Vihar.
Enveloped in a thick layer of impenetrable smog, the natural light is blocked out and a gloomy shadow hangs over the hundreds of high-rise residential flats.
Breathing the air outside triggers waves of nausea and a throbbing headache, while walking up a flight of stairs leaves people breathless.
The sprawling megacity of New Delhi, home to approximately 30 million people, is the most polluted capital in the world.
Earlier this month, the Air Quality Index (AQI) – which measures the level of pollutants – exceeded 1,300 in Sukhdev Vihar, over thirty times the safe level set by the World Health Organization.
Public health experts are exploring a link between pollution and coronavirus
The level of pollution in New Delhi is hazardous all year, thanks to largely unregulated industrial and vehicular emissions, but it peaks during the winter months when thousands of farmers in surrounding states burn crop stubble to fertilise their soil.
As the pollution levels soared in the city in November the number of daily Covid-19 cases also rose, doubling to more than 7,000.
This bucked the national trend, with India as a whole seeing half the number of new daily infections halving from its September peak.
Public health experts are still exploring the link between Covid-19 and air pollution but initial reports indicate a strong correlation.
A Harvard University study of 3,000 districts in the United States found that areas witnessing small increases in pollutants also had a large uptick in Covid-19 fatalities.
In late October, a second study by a group of German researchers found 15 percent of global deaths from the virus could be attributed to long-term exposure to air pollution.
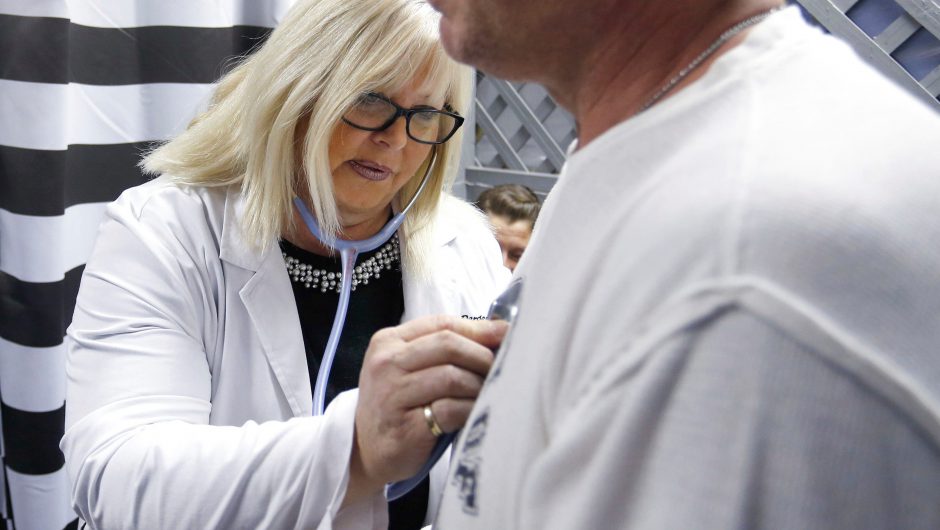
There has been both a 70 percent increase in the number of Covid-19 patients and also far more cases where patients have severe symptoms since pollution began to surge in New Delhi, according to Dr Sumit Ray, a critical care doctor at Holy Family Hospital in Sukhdev Vihar.
Story continues
“The direct effect is on the lungs, prolonged exposure to pollutants makes your airwaves hyper-reactive and they go into constriction, then reacting badly to any infection,” explains Dr Ray.
“Long-term exposure to air pollution causes damages to the air sacs themselves and if someone gets a respiratory infection it becomes much more difficult to fight it off because they already have lung damage.”
The Covid-19 fatality rate in Holy Family Hospital has increased from 3.3 per cent between June and September to 5.05 percent since October 1.
Air pollution can also cause underlying health problems such as heart disease, which in turn can cause the fatality rate from Covid-19 to soar.
A three-month study from the virus epicentre in Wuhan found Covid-19 patients with heart disease had a fatality rate of 16.7 percent, compared to four percent for those without.
Haji Colony next to the Waste-to-Energy plant in New Delhi – Cheena Kapoor
The record-breaking pollution levels in Sukhdev Vihar are exacerbated by a waste-to-energy plant that pumps out toxic gasses every evening.
“I receive a lot of patients with breathing difficulties, especially in October and November” explains Dr M. Rehman, who runs a clinic in the neighbourhood.
“Many inhabitants are asthmatics and are forced to use inhalers, even the younger generation, and I have seen many people die of pulmonary disorders.”
Fazlul Haq, 78, lies motionless in bed waiting for his daughter to change his oxygen cylinder. He considers himself one of the lucky ones.
Mr Haq, who lives 800 metres away from the plant, developed interstitial lung disease (IDL) two years ago and his doctors say there is “no other explanation” for his condition other than long-term exposure to pollution.
IDL causes stiffness in the lungs, making it difficult to breathe and get oxygen into the bloodstream.
“Every year my father faces difficulty during the pollution months but this year was the worst for him after he contracted Covid-19,” explains his daughter, Nausheen Fazal.
Dr. Sumit Ray, the head of critical care, at Holy Family Hospital in New Delhi. – Cheena Kapoor
With his lungs crippled by exposure to long-term pollutants, Mr Haq has spent six weeks battling Covid-19 on an intensive care unit ward in Holy Family Hospital.
To the surprise of doctors he survived but Mr Haq faces an uncertain future, according to Dr Ray, as his lungs are once again exposed to the toxic air.
Despite growing public outrage the Delhi Government has failed to make any dent in lowering pollution levels.
Politicians are cautious to limit industrial growth and attempts to curb stubble burning have failed in surrounding states, with the practice so entrenched.
The Delhi government did not respond to requests for comment.
The Indian government has warned that the city will see 15,000 new Covid-19 cases by December and the fatality rate could rise, due to hospital staffing shortages and a lack of ICU beds.
“I was in the hospital for over two months because my lungs were already only working at 30 percent capacity. I’m now forced to use an oxygen cylinder,” gasped Mr Haq.
“It is because of the pollution and the government’s neglect of it that people like me are suffering.”
Additional reporting by Cheena Kapoor